Sustainable Development Goals
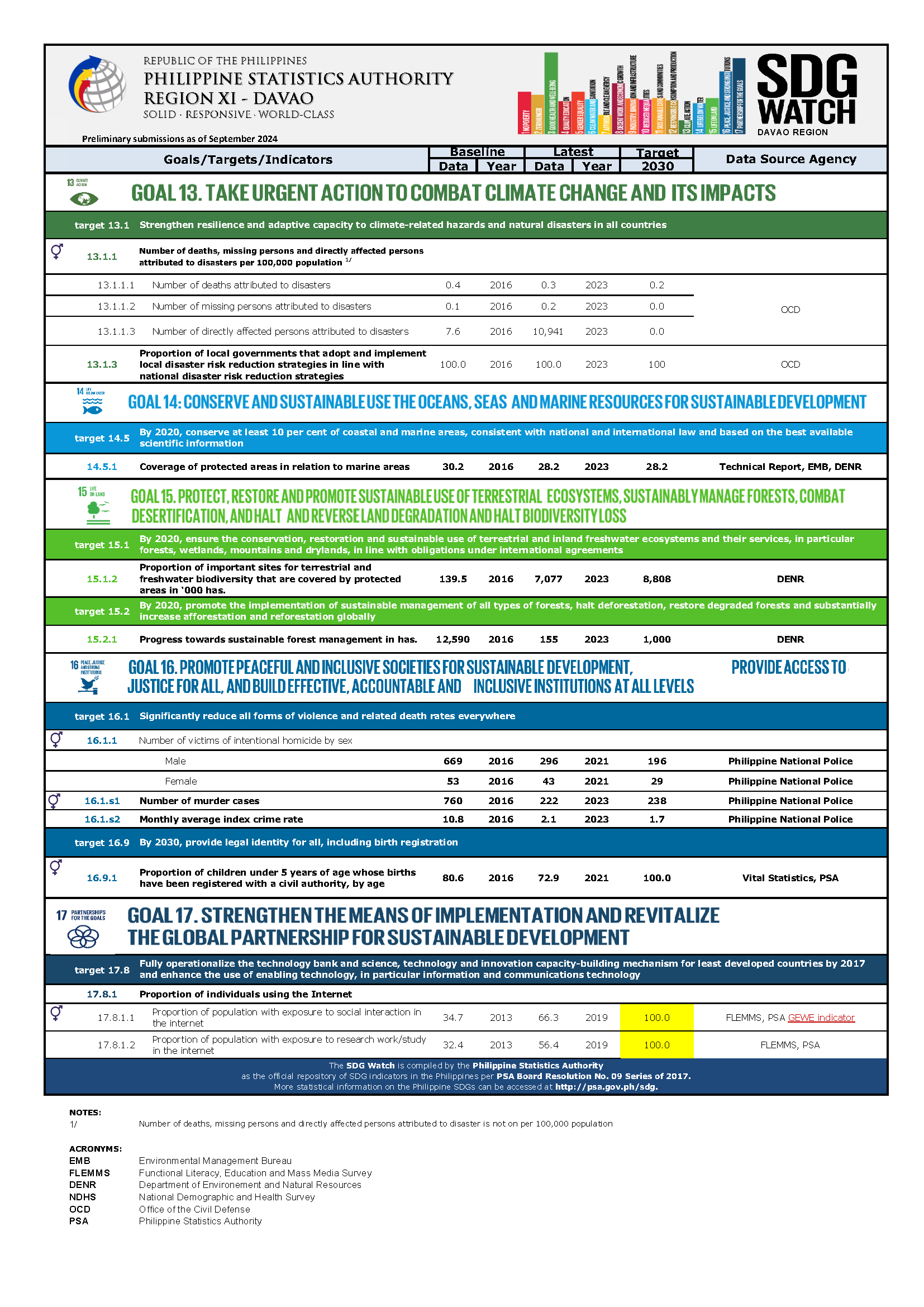
Sustainable Development Goals

SDG Watch Region XI
SDG Pace of Progress - Davao Region
About the SDGs

What is SDG?
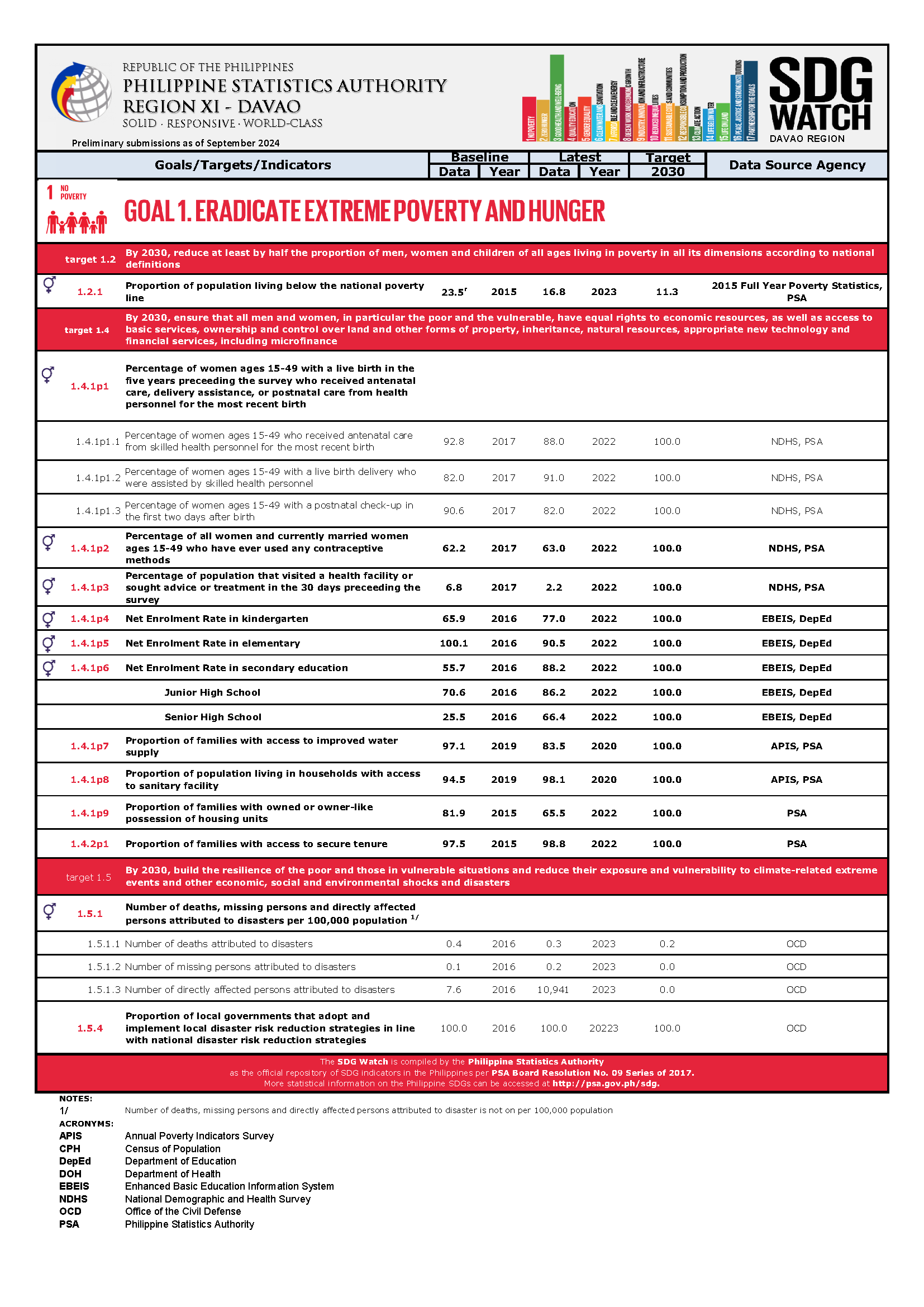
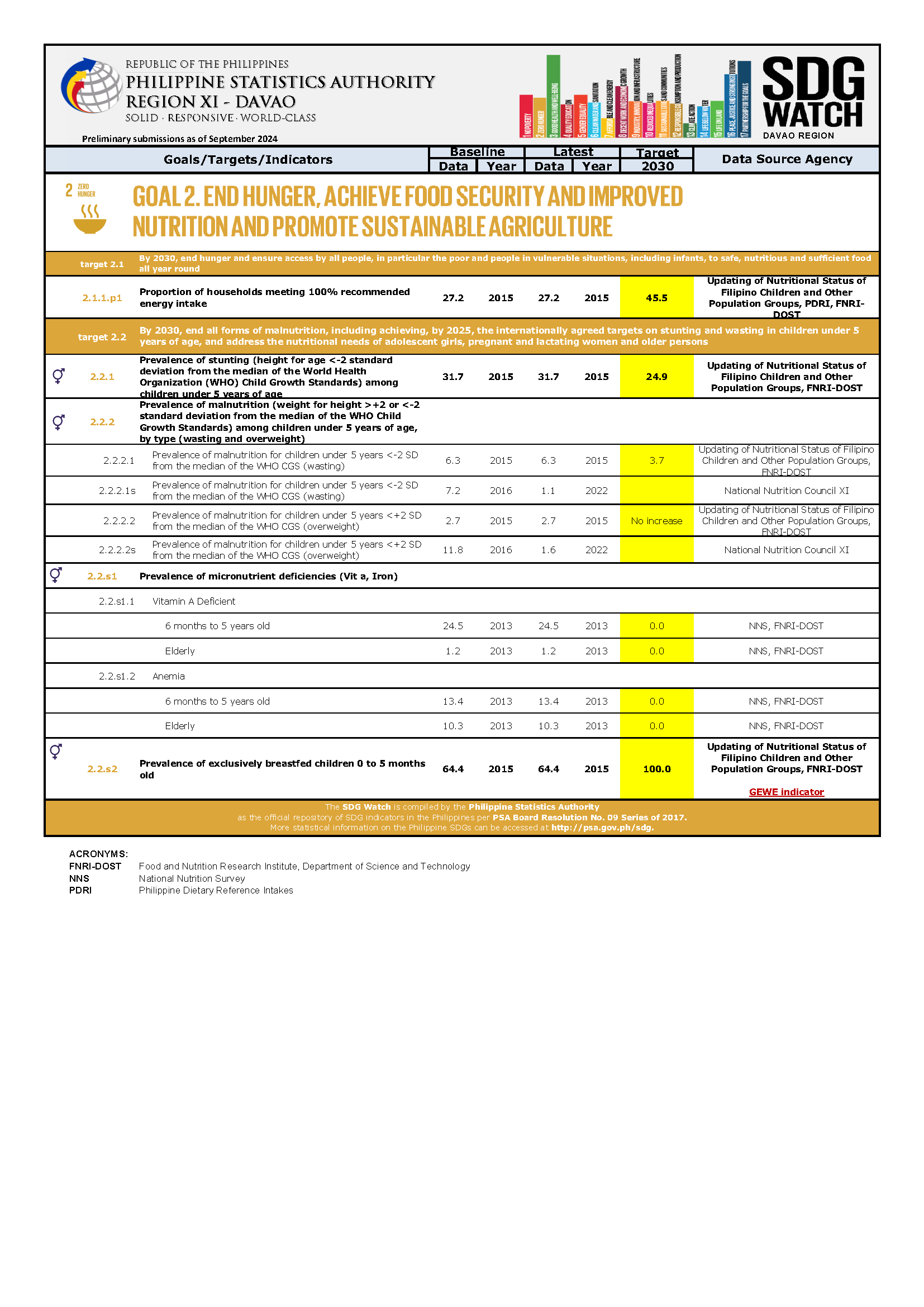
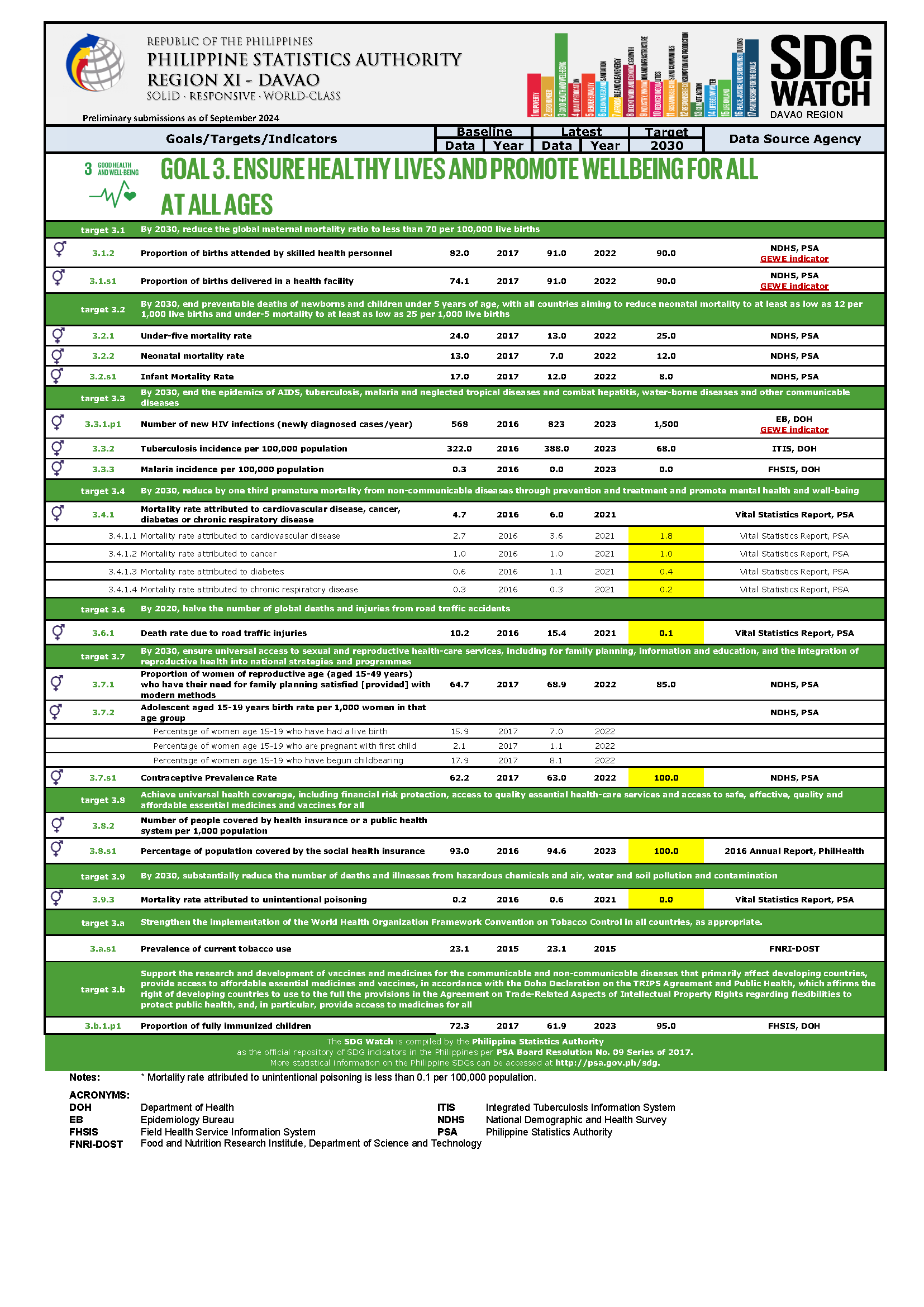
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is also known as the Global Goals. The SDGs are new, universal set of goals, targets and indicators that UN member states will be expected to use to frame country agendas and policies over the next 15 years. It consists of 17 goals, 169 targets and 232 unique indicators. There are 244 indicators listed in the final indicator. However, since nine indicators repeat under two or three different targets, the actual total number of individual indicators in the list is 232.
How can UN Member states achieve the SDGs?
For the countries to achieve the SDGs, they must get not only additional financial resources from both domestic and external sources, but should also formulate policies and set up an institutional environment that will ensure that the resources are used efficiently and effectively.
How are the Sustainable Development Goals different from MDGs?
The SDGs build on the successes of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), which embodies specific targets and milestones in eliminating extreme poverty and the worst forms of human deprivation. The SDGs expanded its scope to 17 goals from the eight (8) goals in the MDGs, which covers universal goals on fighting inequalities, increasing economic growth, providing decent jobs, sustainable cities and human settlements, industrialization, tackling ecosystems, oceans, climate change, sustainable consumption and production as well as building peace and strengthening justice and institutions. Unlike the MDGs, which only targets the developing countries, the SDGs apply to all countries whether rich, middle or poor countries. The SDGs are also nationally-owned and country-led, wherein each country is given the freedom to establish a national framework in achieving the SDGs.
MDGs SDGs Number of Goals 8 17 Number of Targets 21 169 Number of Indicators 60 232 General scope/ focus Social Economic growth, social inclusion & environmental protection Target Developing countries, particularly the poorest Entire world (rich and poor) Formulation Produced by a group of experts Result of consultation process among:
-193 UN Member States
-Civil society
-Other stakeholders